Lawn Frequently Asked Questions
The perfect time to start thinking about your lawn and the care that it might need is as the snow is melting. Maybe you have a lawn that is full of weeds, a lawn that has never been able to sustain grass throughout the summer, or a lawn that is full of animal urine-burned spots. Whatever the case may be, the team at the Essex County Co-Op can help you get your lawn on the right track. Below, we have assembled a list of questions customers frequently ask and their answers. If you need more help, come and see us!
- What are some examples of cool season grasses found in lawns in the Northeast? Bluegrass, Creeping Red Fescue, Turf Type Tall Fescue, Perennial Ryegrass, Annual Ryegrass, and Chewings Fescue are all examples of cool season grasses that grown in the Northeast.
- What are two spreading-type varieties of grass that are found in the Co-Op grass seed blends? The two spreading varietals in the Co-Op blends are Bluegrass and Creeping Red Fescue.
- What are two bunch-type varieties of grass that are found in the Co-Op grass seed blends? Tall Fescue and Perennial Ryegrass are the two bunching varietals found in the Co-Op seed blends.
- When is the best time of year to plant grass seed? Early fall is the best time to plant grass seed. Usually, in our area, this means early September. This ensures the soil is warm, there is adequate moisture, and there is less weed competition at that time of year.
- Why do people put straw over their newly spread grass seed? Straw helps with moisture retention, which is
 critical for seed germination. The straw helps seedlings not get dried out and reduces the possibility that seedlings perish in hot weather.
critical for seed germination. The straw helps seedlings not get dried out and reduces the possibility that seedlings perish in hot weather. - Why is starter fertilizer important? Starter fertilizer provides essential nutrients to seedlings.
- What nutrient in starter fertilizer helps with root development? Phosphorus is essential for root development. The percentage of phosphorus in a bag of fertilizer can be found in the middle of the three numbers on the fertilizer bag.
- What soil temperature is required for common grass seed varietals? A soil temperature of greater than fifty degrees is needed for germination of common grass varietals.
- How long should I wait between fertilizer applications? To avoid nutrient-overloading your grass, you should wait one month between fertilizer applications.
- I don’t have an irrigation system. Can I fertilize in July and August? In a lawn that does not have irrigation, most grass varietals go dormant during hot summer months. Applying fertilizer can damage these grasses. Additionally, some of the nutrients in the fertilizer will break down before they can be used by the grass when it comes out of dormancy in the fall.
- What product can I use to help break up heavy clay soil, lower the pH, and leach away road salt? Adding
 gypsum, such as Fast Acting Gypsum, will help with these three issues. Gypsum is a mineral soil additive that is certified for organic use.
gypsum, such as Fast Acting Gypsum, will help with these three issues. Gypsum is a mineral soil additive that is certified for organic use. - How many pounds of pelletized lime would I apply to my 1,000 sq. ft. lawn to raise the soil pH one point? To increase the pH of your soil one point, use 100 pounds of pelletized lime per 1,000 sq. ft.
- What kind of spreader should I use to apply ground lime to my lawn? A drop spreader would be the best spreader for this application.
- What kind of fertilizer does the Co-Op sell that will make my lawn darker and greener? What mineral does this? The Co-Op sells One Step, which is a unique product made by Green Mountain Fertilizer in Vermont. It is a 12-3-7 fertilizer with pelletized lime. In addition, it has 2% iron which helps lawns turn dark green.
- My lawn is struggling. Is there any benefit to adding compost to it? Topdressing your lawn with compost has many benefits:
- Improves soil organic matter
- Helps break up heavy soil
- Bulks up sandy soil
- Helps sustain beneficial microbes
- Helps break down thatch
- Improves the moisture holding capacity of your soil
- Adds needed nutrients
- Helps fight lawn diseases and pests
- I have seen the Scott’s 4-Step program. What are the four steps and what do each of the steps do? The
Co-Op has a detailed blog on the Scott’s lineup, linked here Scotts 4 Step Program, however, the basic information is below:
- Step 1: pre-emergent herbicide plus fertilizer
- Step 2: weed and feed (post emergent herbicide plus fertilizer)
- Step 3: fertilizer for late spring
- Step 4: fall fertilizer or winterizer
- What is the best time to apply a pre-emergent herbicide and fertilizer to my lawn? Apply a pre-emergent herbicide with fertilizer, such as Scotts Step 1, in early spring. In our area, this is usually mid-April. This product will primarily control crabgrass while feeding the beneficial grasses. A good indication of when to apply this product is when you see yellow flowers blooming on forsythia bushes.
- I have heard I should apply my granular ‘weed and feed’ first thing in the morning. Why is that? It is best to apply a weed and feed product to a wet leaf before two dry days. These two dry days ensure that the product is not washed off. The best time to apply is early in the morning when the leaves are wet with dew.
- What grass seed mix is best for an area that needs a hardy mix? An area that has poor soil, low organic matter, and is not watered would be suitable for a conservation mix. Often these mixes contain Tall Fescue that can have a very deep root system that will survive in poor soils. It is still necessary to have adequate moisture when seeding so germination can take place and the seedlings get established.
- I can’t find grass seed anywhere. What is the availability issue? 2021 was an extremely dry year in the grass seed growing regions. Grass seed mostly comes from the Pacific Northwest which suffered from a severe drought. Because of this drought, they were unable to harvest the seed needed to make grass seed mixes for 2022.
- What pH number is regarded as neutral? 7 is considered a neutral pH. A neutral pH is necessary for optimal nutrient availability.
- What are common grubs found in lawns in our area? In our area, grubs in lawns are usually found as the larval form of two common beetles. The two most common types are grubs are the larvae of Asiatic beetles (Japanese Beetles) and European Chafing Beetles.
- I don’t want grubs. What product should I apply to prevent them and when do I apply it? The Co-Op sells Scotts GrubEx which should be applied in early June. This product stays in the soil for two months and kills the hatching juvenile grubs.
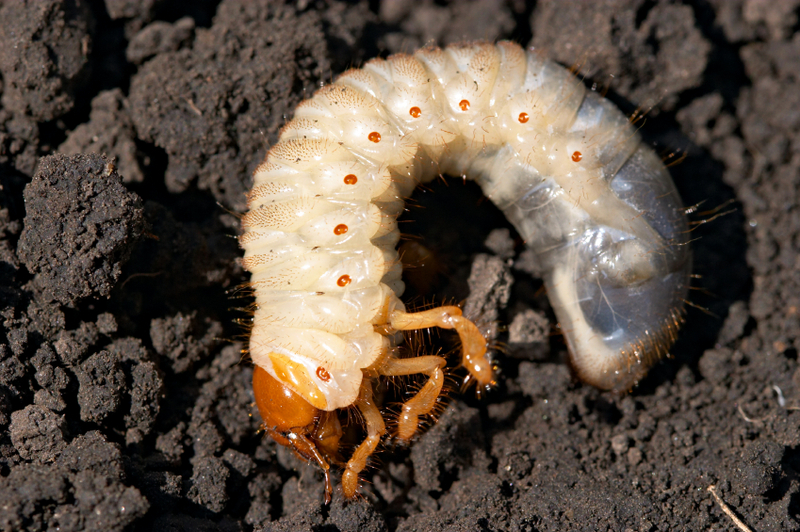

- It is May and I have large grubs in my lawn. What do I do? The large grubs (which have over-wintered in your lawn) and the mature grubs that you might find in the fall can be controlled with Dylox Grub Killer. This is a soluble crystal that needs to be watered into the soil and results can be seen in 24 hours.
- What is red thread and what can I use to control it? Red thread is a common lawn fungus found in the Northeast. Scotts DiseaseEx Granules can be used to control it. Applying a nitrogen fertilizer and removing the infected lawn clippings can help with the control of this fungus.
- What does corn gluten do and what products contain it? Corn gluten attacks a weed just before germination or sprouting. In our area, annual weeds like crabgrass the predominant target. Blue Seal makes Safe ‘N Simple Lawn Food that contains corn gluten. This product also contains 9% nitrogen that will help green up a lawn.
- What are two organic fertilizers that you sell? The Co-Op sells the following organic fertilizers: Safe ‘N Simple Lawn Food,Milorganite,Pro-Gro 5-3-4 Fertilizer, and Espoma Natural Lawn Food.
- Where is milorganite made? Milorganite is made in Milwaukee, Wisconsin.
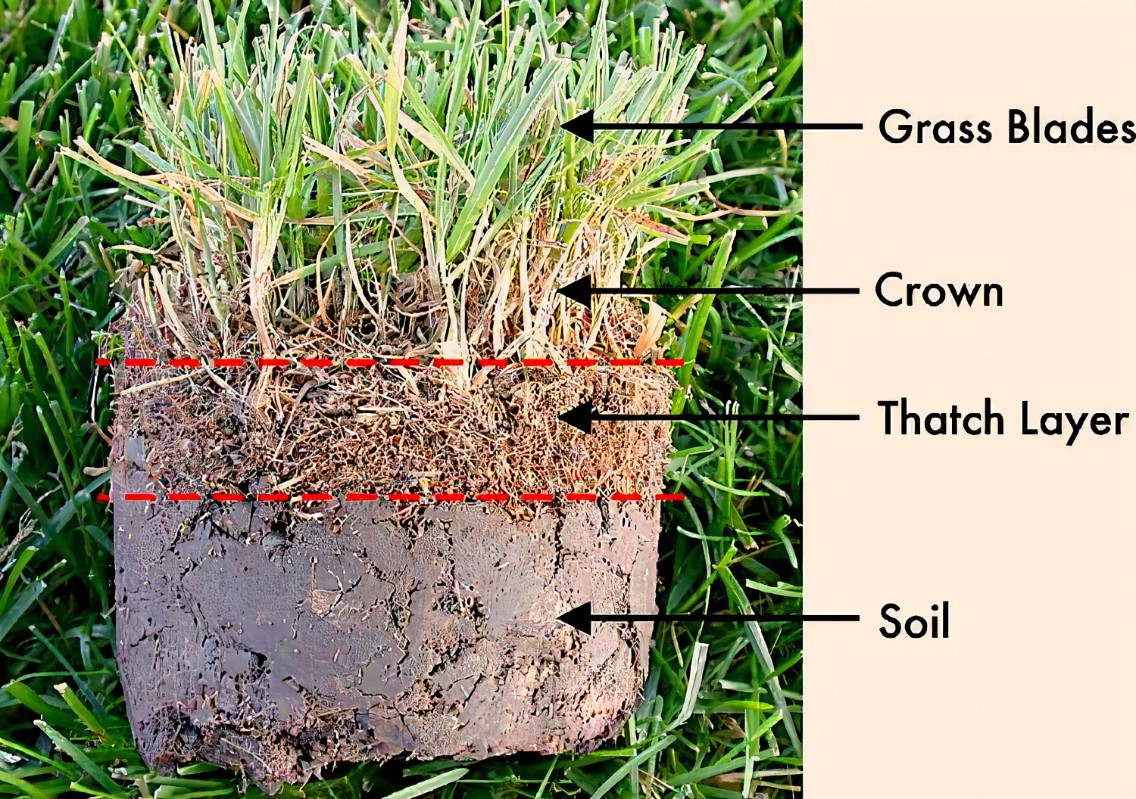
- What is thatch build up and how do I reduce it? Thatch is a matted layer consisting of roots, stems, blades, runners and clippings which forms on top of the soil. Lawn roots can struggle to grow deeper into a heavily thatched lawn and moisture struggles to penetrate into the soil. Excessive fertilizer can create too much material for soil microbes to break down. Aerate your lawn with a de-thatcher, which brings the dead plant material to the surface for removal.
- What is a ‘sticker’ and how does it improve the effectiveness of herbicides? A sticker is a product that helps a product like a herbicide stick to the surface of the targeted weed leaf. This helps with product absorption, thus increasing effectiveness. These products are commonly referred to as surfactants. Bonide Turbo Liquid Spreader-Sticker is an example of a surfactant.
- What are three common broadleaf weeds that I should watch out for in our area? Common broadleaf weeds in our area include: dandelions, plantain, chickweed, clovers, vetch, milkweed, ivy, thistle.
- What is a “plant out of place”? Any plant out of place is a weed.
- I have a nice lawn. Will a soil test help me? Yes, a soil test can help. A soil test can identify nutrient deficiencies, acidic or alkali pH that can affect nutrient availability, and form the basis of fertilizer recommendations. These recommendations help correct soil issues and ensure sufficient nutrients.
- I have 432 sq. ft. that I want to cover in three inches of bark mulch. How much do I order? 432 sq. ft. x .25 (3”/FT) = 108 sq. ft. There is 27 sq. ft. in a yard; 108 divided by 27 = 4 yards needed.
- It is the summer and I just saw my Labrador Sally pee on my beautiful lawn. What do I do? If you watched your pet urinate on the lawn, the best thing to do is thoroughly water the area to dilute the urine and prevent lawn damage.
